Consumable Weight: 0 kg
Welding Consumables Calculator for Butt and Fillet Welds
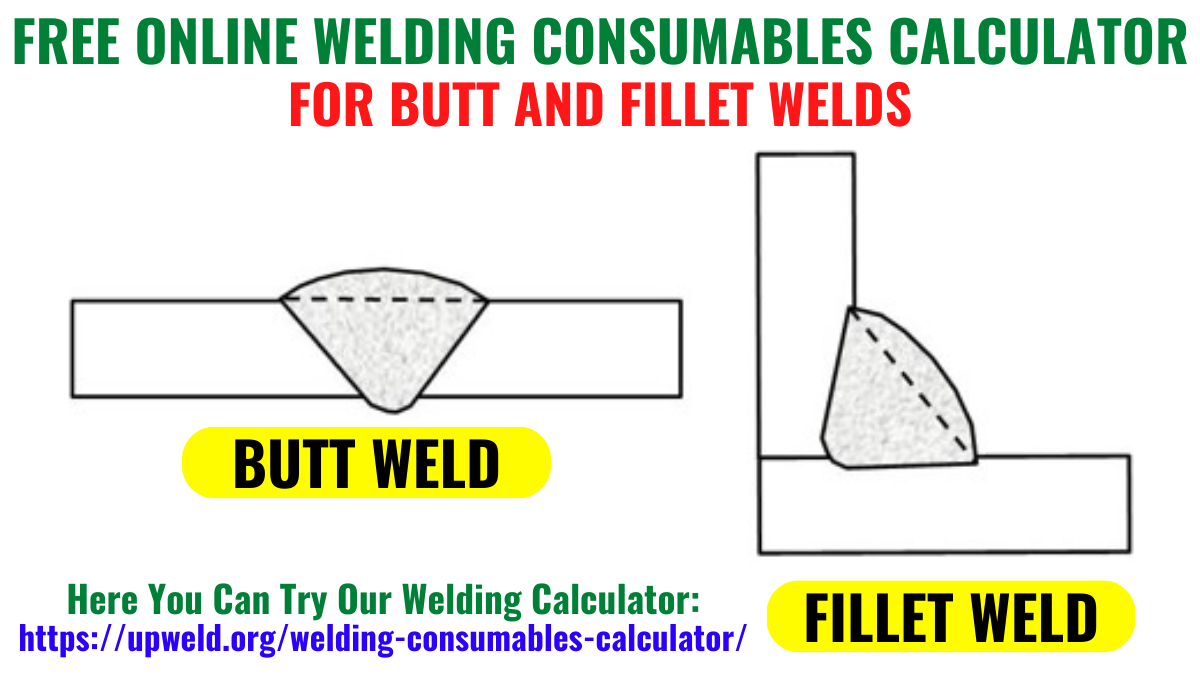
Are you looking for a quick and easy way to calculate welding consumables for your projects? We’ve got you covered! Introducing our Free Online Welding Consumable Calculator for Butt and Fillet Welds – a user-friendly tool designed to simplify the process of determining consumable weights based on material thickness and weld type. Optimize your welding projects with our Free Online Calculator for Butt and Fillet Welds. Easily estimate consumable weights for precise planning.
How to Use the Welding Consumables Calculator?
Step 1: Enter Material Thickness
Begin by entering the material thickness in millimeters (mm) into the designated input field. You can use the up and down arrows or type the value directly. This represents the thickness of the material you’ll be working with.
Step 2: Select Weld Type
Next, choose the weld type from the dropdown menu. You can select either “Butt Weld” or “Fillet Weld” based on your project requirements.
Step 3: Click Calculate
Once you’ve entered the material thickness and selected the weld type, click the “Calculate” button. The calculator will instantly provide you with the estimated consumable weight for your specific welding scenario.
Step 4: Interpret the Results
The calculated consumable weight will be displayed below the button. The result is presented in kilograms (kg). Use this information to plan and optimize your welding processes effectively.
Why Use Our Welding Consumable Calculator?
-
User-Friendly Interface: Our calculator is designed with simplicity in mind. No complex formulas or confusing steps – just enter the information, click a button, and get your result.
-
Accurate Estimates: While the calculations are simplified for user convenience, the tool provides reasonably accurate estimates for consumable weights. It’s a handy resource for project planning.
-
Free and Accessible: We believe in making useful tools accessible to everyone. That’s why our welding consumable calculator is completely free to use, with no hidden fees or subscriptions.
What is the Butt Weld?
Definition: A butt weld is a type of weld that joins two pieces of metal or other materials along a common edge in a single plane. The edges being joined are nearly parallel, and the welding process involves melting the ends of the two pieces and then allowing them to cool, forming a strong and seamless connection.
Applications:
- Commonly used in pipe and tubing systems where a continuous and smooth appearance is desired.
- Ideal for joining two flat or slightly curved metal pieces with edges in close proximity.
Benifites:
- Provides a strong and durable connection.
- Creates a flush and continuous surface.
What is the Fillet Weld?
Definition: A fillet weld is a triangular weld that joins two surfaces at an angle, typically 90 degrees. This type of weld is applied along the corner or edge where two pieces meet, and it forms a concave or convex triangle between the materials.
Applications:
- Widely used in structural applications for joining components at right angles, such as beams to columns.
- Commonly utilized in the fabrication of brackets, frames, and other structures.
Benefits:
- Offers good load-bearing capabilities.
- Provides a smooth transition between the connected surfaces.
In summary, butt welds are used to join two pieces along a common edge in a single plane, creating a seamless connection, while fillet welds are triangular welds that join two surfaces at an angle, commonly used in structural applications. Each type of weld serves specific purposes based on the design and requirements of the project.
Read more: Try our other welding calculators.
Conclusion
Whether you’re a seasoned welder or just starting in the field, our Free Online Welding Consumable Calculator for Butt and Fillet Welds is here to make your job easier. Save time on manual calculations and focus on what you do best – creating strong and precise welds.
Give it a try now and streamline your welding projects with confidence!
Note: This calculator is intended for educational and planning purposes. Actual welding conditions may vary, and it’s always recommended to consult with industry standards and guidelines for precise calculations.